- TESTING BASICS
- AGILE
- REST API
- SQL
- Neo4j
- UFT
- RBA
- ML
- ETL
- CLOUD COMPUTING
- MOBILE TESTING
- TEST STRATEGY
- TEST METRICS & TEST ESTIMATION
- BIG DATA
- INTERVIEW CODE
"A small investment in knowledge that can be money or time pays the best interest" - Amitkumar Singh
HOME PAGE
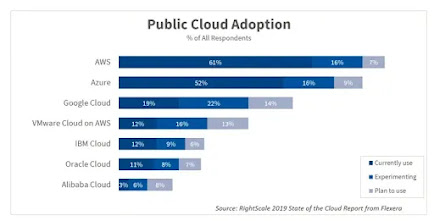
Cloud computing
CLOUD COMPUTING is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user.
CLOUD COMPUTING MODELS:
- IaaS: infrastructure as a service
- SaaS: software as a service
- PaaS: platform as a service
- IaaS: internet as a service
- IaaS works by mobilising a third-party cloud service provider.
- This cloud provider hosts the IT infrastructure.
- That means servers, cloud storage, hardware and virtualisation.
- IaaS delivery is automated.
- System maintenance and data storage is often handed over to the IaaS provider.
- In other words, the service provider hosts the infrastructure on their client’s behalf across different datacenters making up the cloud.
- The client accesses the infrastructure online and uses it for the same purposes that an in-house IT infrastructure would traditionally serve.
- It can be accessed through computers, mobile devices, or virtual machines.
- Developmental testing
- Website hosting
- Data storage and analysis
- Online applications
- High-performance computing
- One step up from IaaS.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) is a cloud-computing platform for the development and building of applications.
- PaaS services usually include developmental tools, middleware, operating systems, databases, and infrastructure.
- SaaS stands for Software as a Service and provides full applications managed in the cloud.
- It provides access to applications over the internet.
- Users no longer have to purchase and install their business applications locally, and can go completely serverless if they desire.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Top features include Simple Storage Services (S3), Glacier and compute services like the Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
- Google Cloud Platform: Offers storage and computing services via the Google Compute Engine.
- Microsoft Azure: Also offers storage and computing services via the Google Compute Engine.
- IBM Cloud: offers next-generation hybrid cloud platforms, with advanced data and AI capabilities.
- Alibaba Cloud: offers integrated cloud products and services for scalable, secure digitisation.
- Oracle Cloud: offers on-premises, high-performance computing running cloud-native.
- Virtustream: offers enterprise-class cloud services for complex IT landscapes.
- CenturyLink: offers communications, network services, cloud, and managed service solutions.
- Rackspace: offers proven multicloud solutions across apps, data, and security.
ETL
- Data is extracted from online transaction processing (OLTP) databases, today more commonly known just as 'transactional databases', and other data sources.
- OLTP applications have high throughput, with large numbers of read and write requests.
- They do not lend themselves well to data analysis or business intelligence tasks.
- Data is then transformed in a staging area.
- These transformations cover both data cleansing and optimizing the data for analysis.
- The transformed data is then loaded into an online analytical processing (OLAP) database, today more commonly known as just an analytics database.
- Identify the systems to be reconciled. This may include a data warehouse, data lake, and/or other data sources.
- Identify the data to be reconciled. This may include all data in the systems, or a specific subset of data.
- Identify the change that was made to one of the systems. This may be a new data source, a change to the data schema, or a change to the data processing logic.
- Generate test cases. This will involve identifying the different ways in which the data could be affected by the change, and creating test cases to verify that the data is still synchronized after the change.
- Execute the test cases. This may involve running Glue jobs, using a third-party tool, or manually comparing the data in the two systems.
- Analyze the results. If any of the test cases fail, then the cause of the failure needs to be investigated and fixed.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Machine Learning

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BASIC TERMS
Note: All are used to find Average
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Data distribution:
When line of Mean, Median and Mode are at coincides then data is said to be distributed normally.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 types of Analysis:
- Diagnostic: What happened?
- Descriptive: Why happened? BI reporting
- Predictive: What can happen?
- Prescriptive: What can better happen?
Types of Machine Learning:
1) Data collection
2) Data processing, tabulation & presentation
3) Measure of central tendency (Average=Mean, Median, Mode)
4) Measure of dispersion: Standard deviation and variance
5) Correlation
6) Regression (Finding dependent- X axis & Independent feature- Y axis)
7) Advance statistical techniques
Outliers in Box plot (Eg:)
Person who is having very less salary (Cleaning staff)
Person who is having very high salary (CEO)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Minimum Score
The lowest score, excluding outliers (shown at the end of the left whisker).
Lower Quartile
Twenty-five percent of scores fall below the lower quartile value (also known as the first quartile).
Median
The median marks the mid-point of the data and is shown by the line that divides the box into two parts (sometimes known as the second quartile). Half the scores are greater than or equal to this value and half are less.
Upper Quartile
Seventy-five percent of the scores fall below the upper quartile value (also known as the third quartile). Thus, 25% of data are above this value.
Maximum Score
The highest score, excluding outliers (shown at the end of the right whisker).
Whiskers
The upper and lower whiskers represent scores outside the middle 50% (i.e. the lower 25% of scores and the upper 25% of scores).
The Interquartile Range (or IQR)
This is the box plot showing the middle 50% of scores (i.e., the range between the 25th and 75th percentile).
- Numpy: Used for Multidimensional Array,
- Pandas: Used to read from different data sources.
- Matplotlib: Visualisation library
- Seaborn: Visualisation library
- Scikits: Contains ML algorithms
RBA
RISK BASED AUTHENTICATION:
RBA is a form of strong authentication that calculates a risk score for any given access attempt in real time, based on a predefined set of rules. Users are then presented with authentication options appropriate to that risk level.
Risk scores are based on a number of contextual factors related to the access attempt, including:
- Login Device: Is this a registered or known device? Is there an associated fingerprint that can verify the device?
- IP Reputation: Is this a known or suspect IP address or subnet associated with bad actors?
- User Identity Details: Is the user’s information being presented the same as the information stored in the directory or user store?
- Geolocation: Is the user’s current geographic location known to be good or bad? Are there certain locations to which you simply need to block access or should access only be granted if at a specific facility?
- Geovelocity: Does the user's location and time of login make sense given the time and location of the last login attempt? I.e., you can’t log in in San Francisco at 1:00 PM PST if you just logged in from Boston at 2:30 PM EST.
Risk scores also can and should include other actors, such as:
- Personal Characteristics: Time with company, role or job levels, history of security incidents and certifications, granted entitlements, etc. I.e., if a user fails to pass an internal security certification exam or falls prey to an internal phishing test, the user is automatically required to “step up” to two-factor authentication.
- Application or Data Sensitivity: How critical or sensitive is the target system or data being accessed? Do certain systems mandate a second or third form of authentication? For example, an intern should not have access to any financial systems.
- Number of Attempts: Fail three times and your account is locked until you call support.
- Push authentication: Push authentication is usually combined with the use of a password, but can be used in lieu of a password. Instead, users verify their identity by responding to a push notification that is sent to their mobile devices.
- PushOne Time Password (OTP) and Time Bases One Time Password (TOTP)
- FIDO U2F tokens: U2F tokens are typically used for VPN authentication, web-based access, and Windows logon. The user simply inserts his or her U2F token into a USB slot (optional NFC and Bluetooth tokens are available), enters or confirms his or her username when logging into RapidIdentity, then presses the U2F token button, and enters a password or PIN.
- Smart card with PKI: Particularly if cards are already in use for facility access or other purposes.
- Fingerprint Biometrics: Bio-metric authentication.
REST API
REST APIs enable you to develop any kind of web application having all possible CRUD (create, retrieve, update, delete) operations.
Guarantees following principles:
1) Client-Server application
2) Statelessness: No change to actual state of accessed resource
3) Cacheable: Client decided whether cache needs to be generated or not
4) Layered Architecture
5) Code on demand: Servers allows to send code to client anytime
6) Uniform interface
API Testing: Testing application at business layer
A URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) is a string containing characters that identify a physical or logical resource. URI follows syntax rules to ensure uniformity. Moreover, it also maintains extensibility via a hierarchical naming scheme.
Eg: https://uatapi.gst.gov.in/bankapi/v0.2/payment (URL+API Name+Version+Module)
HTTP Methods:
1) GET
Use GET requests to retrieve resource representation/information only – and not to modify it in any way.
GET and HEAD methods should be used only for retrieval of resource representations.
Response code:
Data found: 200 (Success)
Data not found: 404
Request is not correctly formed: 400 (Bad Request)
2) POST
POST methods are used to create a new resource into the collection of resources.
Response code:
Post Creation: 201
Resource that can be identified by a URI: 200
No Content: 204
3) PUT
Use PUT APIs primarily to update existing resource (if the resource does not exist, then API may decide to create a new resource or not)
Complete updation/Replace
Post Creation: 201
if an existing resource is modified: 200
No Content: 204
4) DELETE
DELETE operations are idempotent. If you DELETE a resource, it’s removed from the collection of resources.
Response code:
Successful response: 200
If the response includes an entity describing the status: 202 (Accepted)
Calling DELETE on a resource a second time: 404 (Not found)
5) PATCH
HTTP PATCH requests are to make partial update on a resource.
PATCH method is the correct choice for partially updating an existing resource, and PUT should only be used if you’re replacing a resource in its entirety.
Response code:
Method not allowed: 405
6) HEAD
Fetch only headers.
7) PATCH
Used for partial update not complete like PUT method.
8) OPTIONS
- Used for checking all options available in API
- Used in exploratory testing
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100- Information messages
200- Successful
300- Redirection (Request has more than 1 response from which Client should select one)
400- Client error
500- Server error
Code | Status | Description |
200 | OK | The request was successfully completed. |
201 | Created | A new resource was successfully created. |
400 | Bad Request | The request was invalid. |
401 | Unauthorized | The request did not include an authentication token or the authentication token was expired. |
403 | Forbidden | The client did not have permission to access the requested resource. |
404 | Not Found | The requested resource was not found. |
405 | Method Not Allowed | The HTTP method in the request was not supported by the resource. For example, the DELETE method cannot be used with the Agent API. |
409 | Conflict | The request could not be completed due to a conflict. For example, POST ContentStore Folder API cannot complete if the given file or folder name already exists in the parent location. |
500 | Internal Server Error | The request was not completed due to an internal error on the server side. |
503 | Service Unavailable | The server was unavailable. |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eg: POST/ PUT request
Body will uniformly consist of three
attribute:
· Action
· Data
· Sign
JSON Payload will be similar to below format
{
“action” : “Action as per requirement”,
“data” : “ Payload ”,
“sign” : “Above data can be encrypted through a digital
certificate”
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SCENARIOS FOR TESTING IN API:1) Endpoints are correctly named, that resources and their types correctly reflect the object model, that there is no missing functionality or duplicate functionality, and that relationships between resources are reflected in the API correctly.
2) API test actions
2.1) Verify correct HTTP status code
2.2) Verify response payload
2.3) Verify response headers
2.4) Verify correct application state
2.5) Verify basic performance sanity
3) Test scenario categories
- Basic positive tests (happy paths)
- Extended positive testing with optional parameters
- Negative testing with valid input
- Negative testing with invalid input
- Destructive testing
- Security, authorization, and permission tests
4) Test flows
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------